What is Endocrinology?
Endocrinology is the study of hormones in the body. The endocrine system is made up of a network of glands which secrete hormones to regulate many bodily functions, including growth and metabolism. Endocrine diseases are common and usually occur when glands produce an incorrect amount of hormones (i.e. too much or too little).

The Endocrine Glands
The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete chemicals called hormones to help your body function properly. Hormones are chemical signals which are secreted into the bloodstream that coordinate a range of bodily functions.
The glands and the hormones they produce are:
Pituitary Gland:

Sometimes called the "master gland," the pituitary gland secretes and stores hormones, which it uses to regulate other glands.
• Prolactin
• Follicle-Stimulating Hormone(FSH)/Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
• Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
• Growth Hormone (GH)
• Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Thyroid: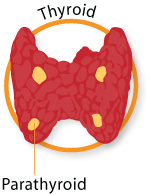
The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls how sensitive the body is to other hormones.
• Thyroxine (T4)
• Triiodothyronine (T3)
Parathyroid:
Parathyroid glands control the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones.
• Parathyroid Hormone
• Calcitonin
Adrenal:
The adrenal glands are chiefly responsible for releasing hormones in response to stress and maintaining salt/water balance.
• Cortisol
• Epinephrine/Norepinephrine (NE)
• Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate (DHEA-S)
• Aldosterone
Pancreas:
The pancreas creates enzymes to aid digestion and hormones to help regulate blood sugar levels.
• Insulin
• Glucagon
• Somatostatin
Ovaries:
The ovaries are a pair of glands in the female reproductive system where eggs are produced and estrogen is manufactured.
• Estrogen
• Progesterone
• Testosterone
Testes:
The primary functions of the testes are to produce sperm and make testosterone.
• Testosterone
Endocrine Gland Disorders
Pituitary Disorders:
• Tumors
• Pituitary hormone deficiencies
• Pituitary hormone excesses
Thyroid Disorders:
• Nodules
• Goiter
• Multinodular goiter
• Hyperthyroidism
• Hypothyroidism
• Thyroid cancer
Parathyroid Disorders:
• Tumors
• Hyperparathyroidism
• Hypoparathyroidism
Adrenal Gland Disorders:
• Tumors, cancer, nodules
• Cushing's syndrome
• Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison's disease)
• Aldosteronism
• Pheochromocytoma
Diabetes:
• Medication and insulin management
• Insulin pump referrals, education and instruction
• Continuous glucose sensors
• Hypoglycemia
• Immunizations against influenza and Pneumovax
Metabolic Bone Disorders:
• Osteoporosis/Osteopenia
• Osteomalacia (vitamin D deficiency)
Testes:
• Erectile dysfunction (ED)
• Testosterone deficiency
• Testosterone excess
Ovaries
• Menopausal symptoms
• Polycystic ovarian disease
Lipid Disorders:
• Hypercholesterolemia
• Hypertriglyceridemia
• Mixed disorders
• Rare genetic diseases of lipid metabolism
![]()












